Advertising is one of the essential pillars of any business and brand. But for some (if not many), they wouldn’t know where to start, even with an already-running business. Google Ads is a fantastic tool to advertise on, well, Google, and its associated sites. We’re here to show you all types of Google ads and how to set up an account of your own for your e-commerce business.
What is Google Ads?
Google Ads is Google’s pay-per-click (PPC) advertising platform and solution for advertising on the search engine results pages (SERPs). It’s a paid service that helps you run and organize ad campaigns on the two largest search engines in the world: Google and YouTube. But you can also run ads on other Google sites like Gmail.
It can’t be overstated just how great a decision it is to use Google Ads to advance your brand. It is much more than just increasing revenue and reach. It’s also about businesses wanting to stay competitive. There are around 3.5 billion Google searches a day, and each search is an opportunity for brand recognition and customer acquisition.
And that’s the main point of it all: conversions, sales and leads.
Advertising with Google Ads also means you should understand its campaign structure. “Campaigns” are what you use to organize and keep track of your ads.
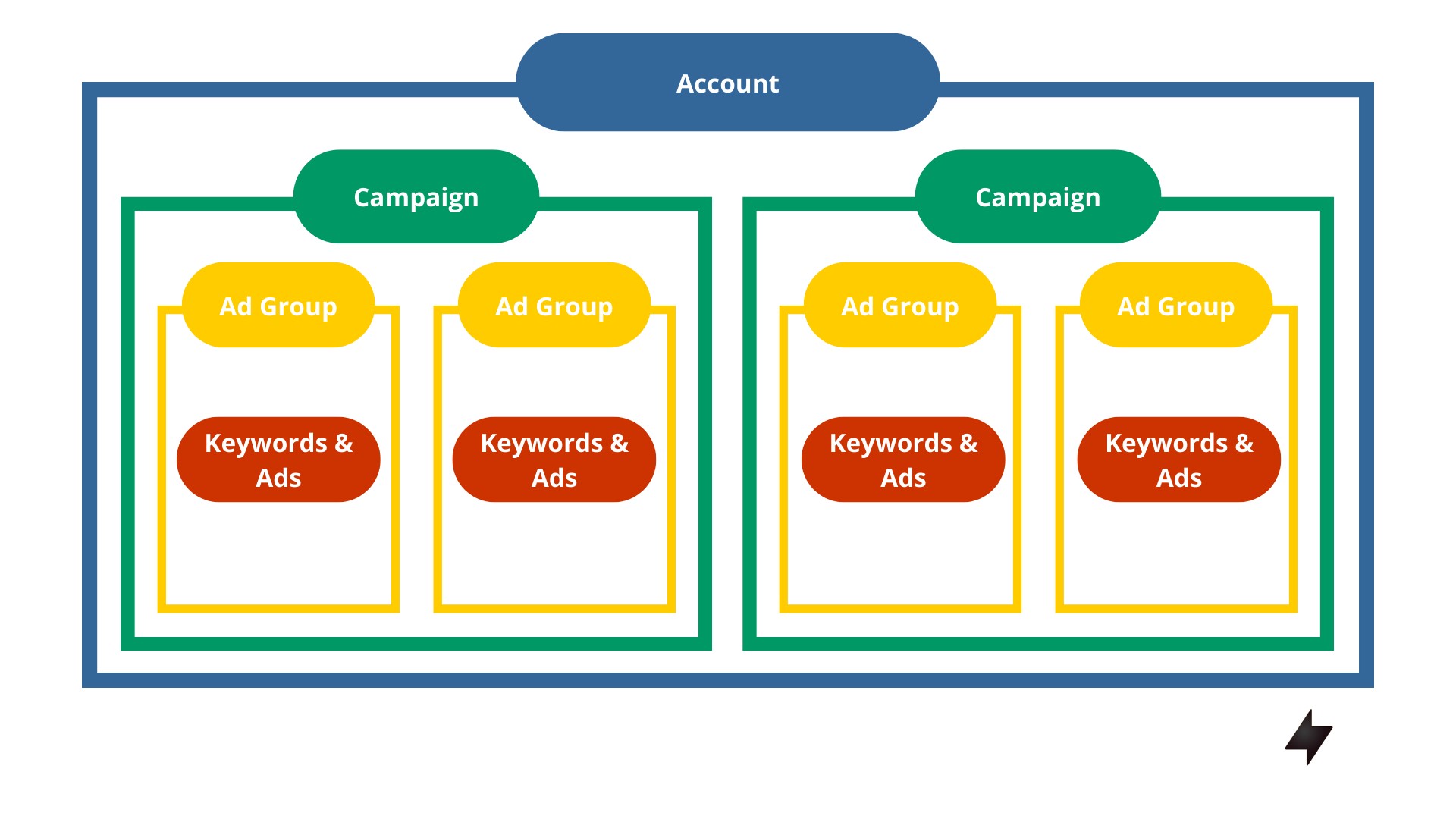
A single Google Ads can run multiple campaigns at a time. Each campaign has multiple ad groups, which in turn houses keywords, ad texts and your landing pages. The upside to having campaigns structure your ads account is that you can have different target audiences and do test runs.
Google Ads campaign structure is quite similar to how Facebook does it. Facebook Ads manager is the site’s own advertising tool. And with the Ads Library, you can compare and track your ads alongside competitors’.
Types of Google Ads
Google Ads presents to you a number of different ad formats that you can decide on using that suits your business and brand best. Here’s the rundown on those ad types you commonly see on Google:
1. Expanded Text Ads (ETAs)
It used to be called standard text ads. When it was changed to ETA, it reflected the word “expanded” in its name. ETAs offer you to have up to 3 headlines, 2 descriptions, and extensions that display phone numbers and links to the different pages on your website.

2. Dynamic Search Ads (DSAs)
DSAs are a type of automated ads that automatically display ads with your website’s contents. With a well developed website, clear product categories and inventory, this type of ad can save you a lot of time. Basically, a DSA targets a user searching for a similar product/service to yours. Although keep in mind, that automation means little control over how the ad turns out. But Google does its best to keep the ad relevant to your specifications.
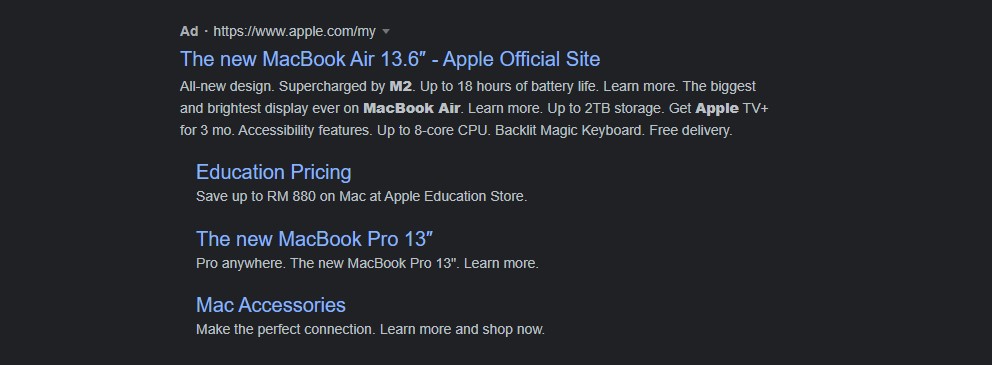
3. Responsive Search Ads (RSAs)
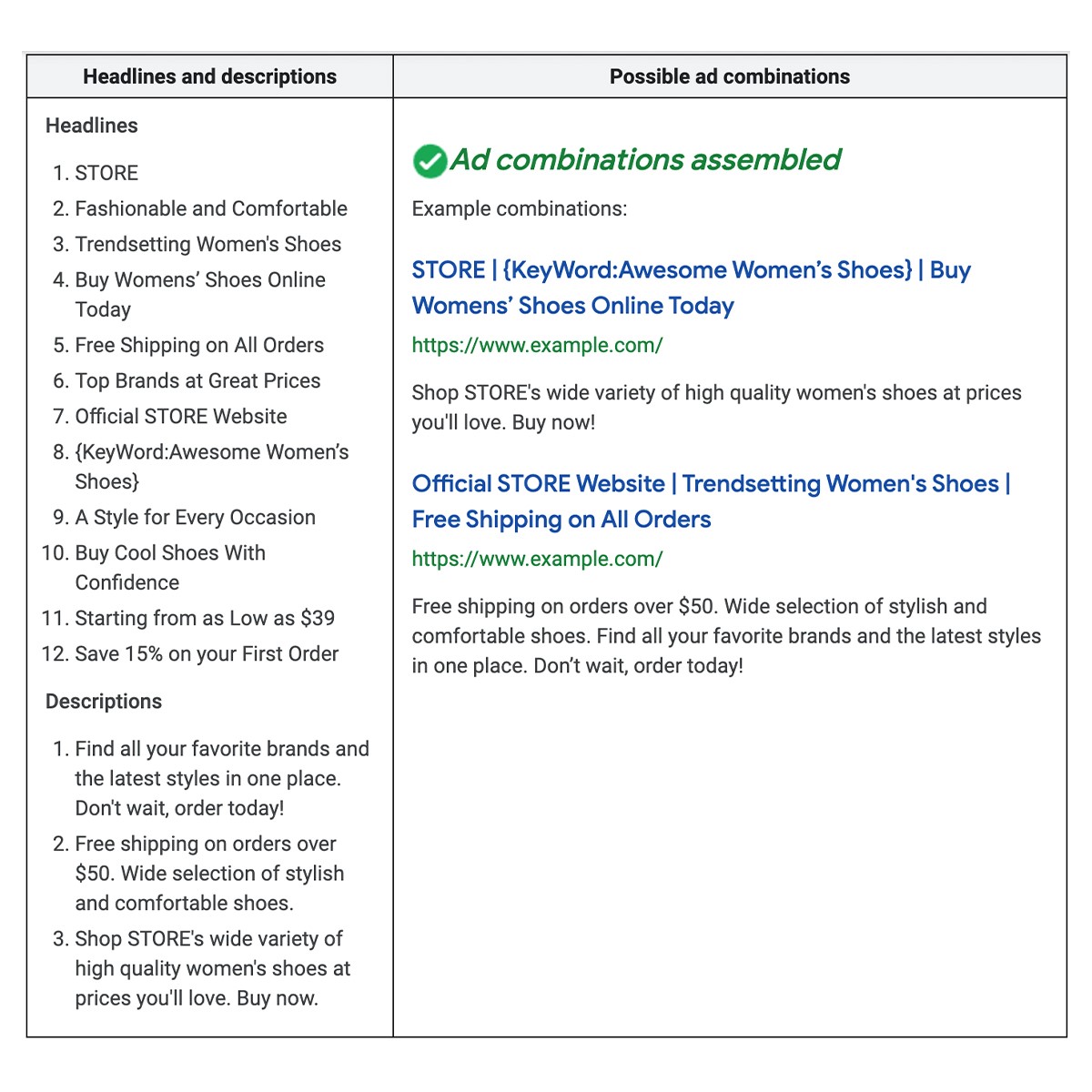
RSAs expand on ETAs even more. There are more options: 14 headlines and 5 descriptions, so you can experiment and test different variations of your ads without having to create them separately. Google will then try different combinations until it gets the most ideal one, which will best engage and effectively reach your potential customers at the best time.
4. Image ads
Image ads or display ads are run by Google’s Display Network. Meaning, they show up on Google’s partner websites that provide ad spaces and Google will then choose the website that your target audience visits often to show those ads. Image ads can be static or interactive and are more inclined for brand awareness campaigns.
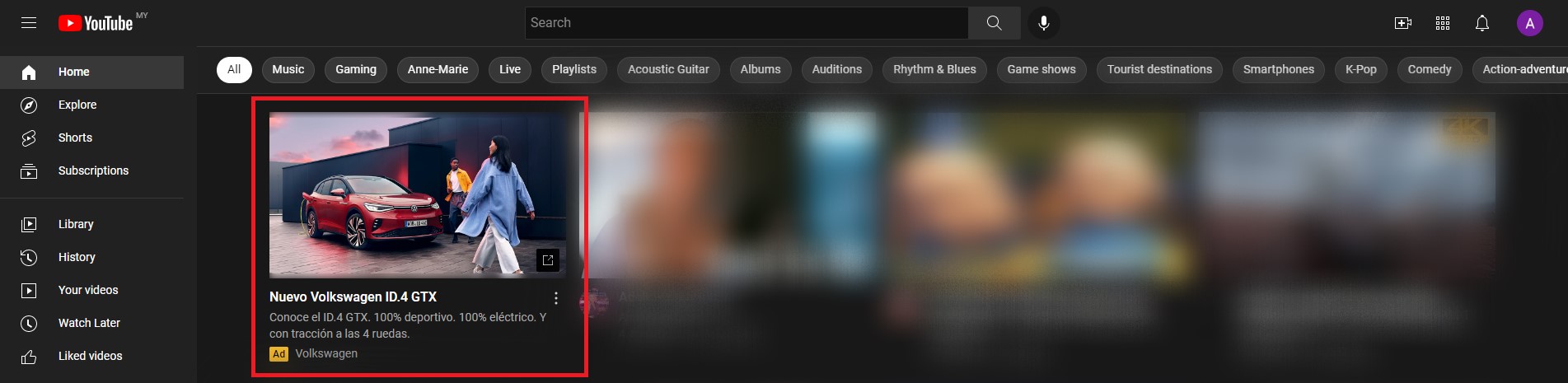
5. Video Ads
If you’ve ever spent a fair amount of time on YouTube, then you’ve definitely seen a video ad, be it at the beginning, in the middle, or at the end. Video ads are actually a more engaging experience to users. Video advertising is very lucrative and if you have the budget, it’s highly recommended. Especially since one-third of all activities online is consuming videos with 500 million hours of watch time on YouTube alone.

6. Product shopping ads
Product shopping ads appear at the very top of the search engine results page (SERP). These ads show the item that’s on sale with the product image, name/title, price and the link to your store. The information displayed, Google retrieves it from your Google Merchant Center account through the product feed.
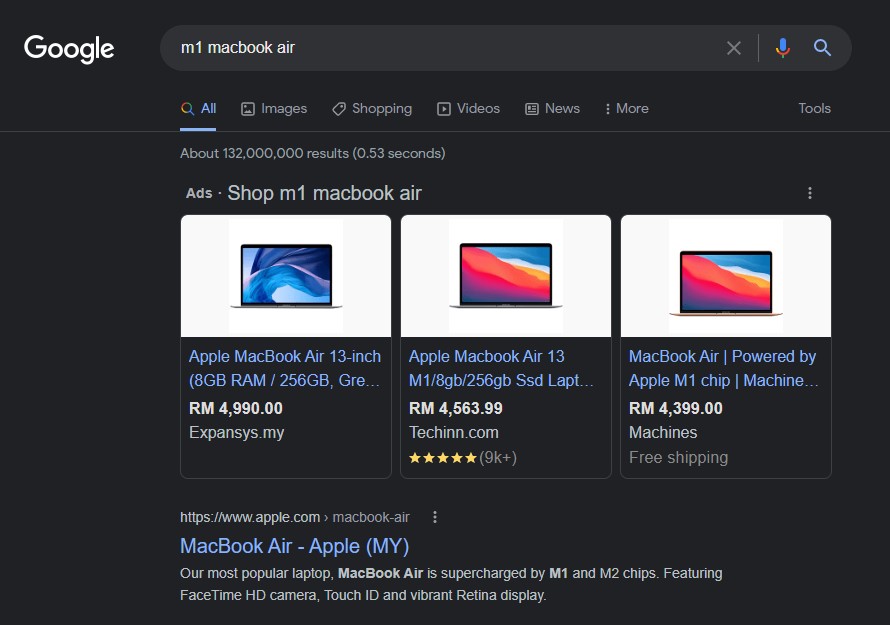
The benefits of using Google Ads
So why should you even use Google Ads in the first place? While it can seem to be taxing at first, delving into Google Ads and using it to your advantage does give you a number of benefits that should make the time invested in it, well worth it:
1. Control your costs
Be it high or low, the budget you set when advertising on Google and with Google will give you results and returns that are worth your investment. Google Ads is a flexible platform cost-wise for businesses of all shapes and sizes.
You can start small and low with your ad costs and multiply your profits through ads by spending more as you grow. Compared to traditional advertising, Google Ads is more cost-effective and just how much control you have over your finances on your ads.
2. Increase brand awareness
As we said earlier, display ads are more appropriate for your brand awareness campaign. Combine that with search ads and the algorithm targeting the right people at the right time, your business covers more ground in a shorter amount of time. Hence, increasing your brand awareness.
The data you receive about your customers’ behaviors online from your time advertising with Google Ads, can lead you to exciting partnerships with content creators and influencers. Also leading to potential sponsorship deals that further raises brand awareness.
3. Target your ads
Using targeted advertising like with keywords and image ads, is a very powerful method of finding potential customers at the best time as they’re searching online for products and services similar to yours. Targeting online users to optimize your resources and time is what Google Ads is great at.
The upside of keywords, for example, is that you can funnel your way to getting more specific search terms. With enough data and analytics, you’ll access more specific keywords that are sure to trigger your ads. This leads to less competition and less costs.
Targeting your desired audience also includes their age, gender, income, locations and languages. Video ads on the other hand have additional placements – where’s best to place your ad – and topics – so that your ads match specific subject matters.
4. Manage your campaigns
It’s not just your finances. Google Ads serves you a lot of opportunities to be at the helm and manage your ad campaigns. You can fully control and optimize your ad campaigns to your liking to get the most, in terms of results, out of it. Just a few examples include: how much to spend, when to start and stop ads, campaign goals, conversions, your target audiences and how your ads look. On top of this, as you’ll see, Google Ads is very beginner-friendly.
5. Local advertising
When running a small to medium size business, your market is most probably local and within your relative vicinity. And when relying on local traffic for your sales, Google Ads will benefit you by advertising your ads locally. This increases local traffic to your business and raises your local brand awareness.
Local searches have high purchasing intent and customers want to fulfill their needs near them and with acceptable convenience. Local advertising is possible when Google Ads utilizes approximate locations and ranges and Google Maps, to then target the closest potential customers to you. And for them, the closest brand – which is you.
6. Fast results
Google Ads can guarantee you quick results from your advertising efforts. Before that, even setting up and getting started is fast, which can happen in a matter of hours. Then, in the next couple of days, you can analyze how your ads are performing to make some adjustments and optimizations. This also in turn makes learning what works and what doesn’t equally as fast.
How to create Google Ads campaign
And so, we’ve looked at what Google Ads is, the types of ads that you get with Google, and why and how it benefits your brand and business. Now, we’ll actually get to the part on how to create your own ad campaign with Google Ads.
Don’t fret! Setting up with Google Ads may seem to be somewhat daunting, but it actually isn’t. As we’ve mentioned earlier, Google Ads is very beginner-friendly. Just follow our easy guide here and you’re good to go:
1. Create a Google Ads account
The first thing you’ll need to do, like with all online things, is to create a Google Ads account. You can go to ads.google.com (Google Ads website) to do this and click “Start Now”. Then, sign in with your Google account or create a new one if you prefer.
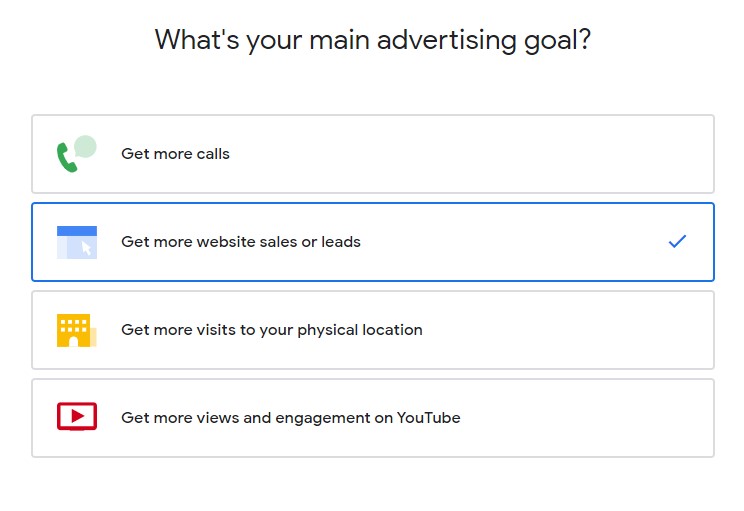
2. Set your campaign goals and types
You’ll then get a screen prompting you to choose a main advertising goal. These prefab options will tie in closely with your ad campaign, so choose the one that’s most relevant to your personal goals.
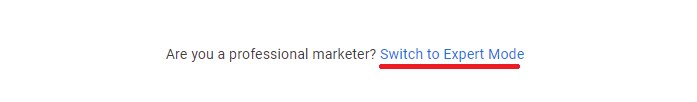
If you’re not really feeling what Google has already prepared (which, to be honest, means you’ll be letting Google set up most of the things already, for you), you can choose the “Switch to Expert Mode” option at the bottom.
We recommend choosing this option because this gives you more control over your campaigns.
You’ll now have the option to set up your campaign objectives/goals. You have the options presented to you, or you can choose to “Create a campaign without a goal’s guidance”.
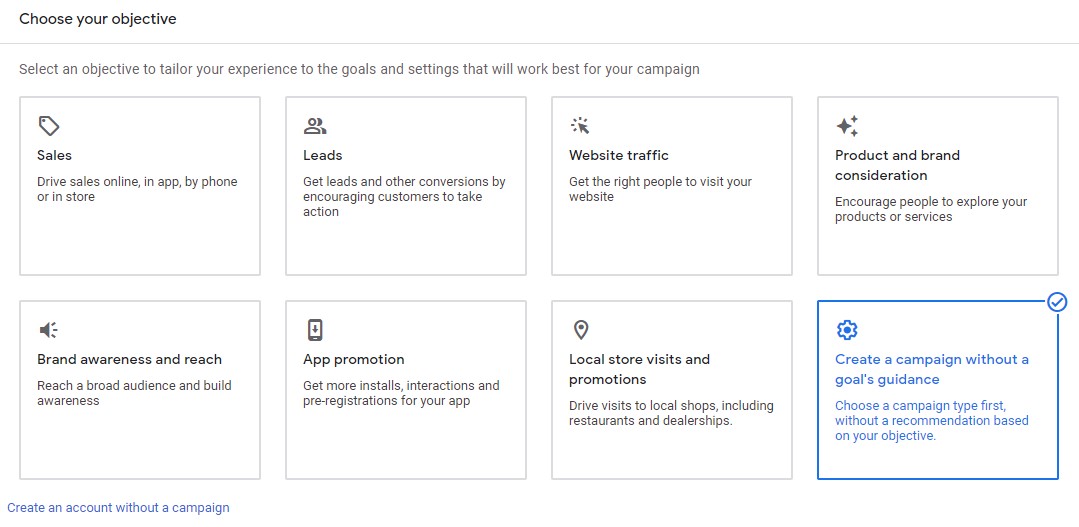
Again, this option will give you more sway and control over your campaign, so we recommend going with this.
Campaign Types
This then brings us to the types of campaigns you want to run.
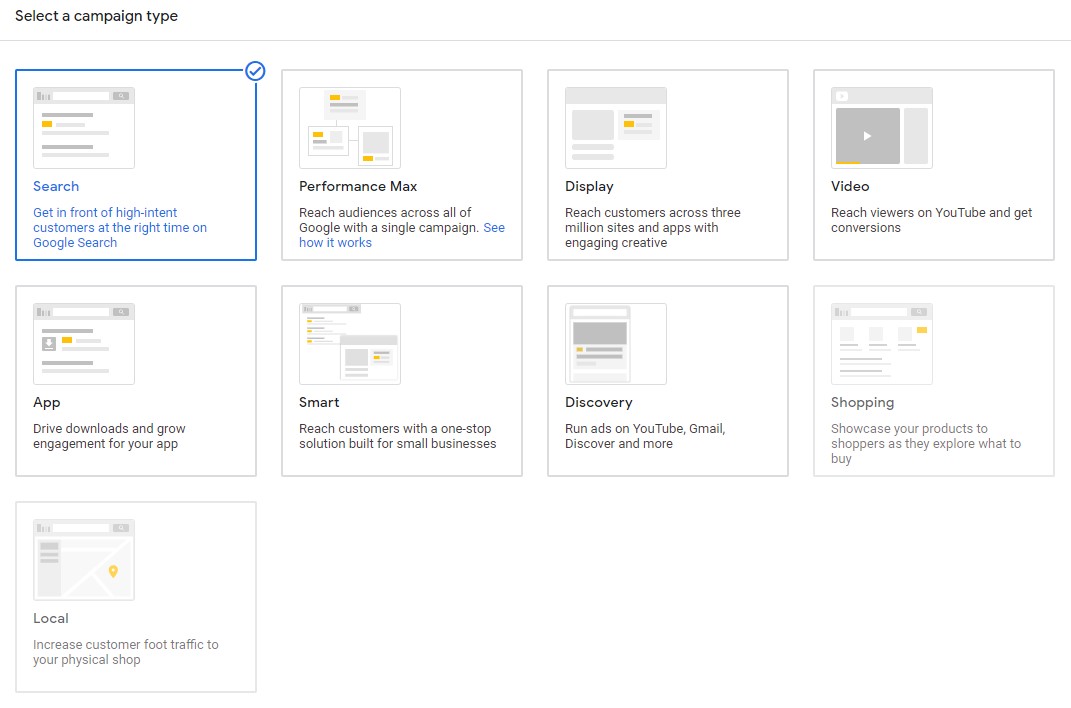
You have a total of 9 campaign types to choose from. As a heads up, our guide will focus on setting up your “Search” campaign. This is the best place to start if you’re new to PPC advertising and it’s the easiest and most basic form of advertising on Google.
But for your benefit down the road, we’ll still briefly look at the other campaign types you’ll be choosing later on as you get more familiar with it all. So about the campaign types:
- Search
This is the campaign that’s used to show text ads that you see on the search results pages of Google. You choose keywords related to your brand that target search queries (the words users type in when googling). This then triggers your ads.
- Performance Max
Performance Max allows you to access all of your ads from a single campaign. Basically, if user searches don’t match up with the Search keywords you set up, Google will select the next best ad besides the Search one to trigger. All of this is automated and is done based on your original specifications.
- Display
There are more than 2 million websites that Google has partnered with and has access to. These websites are where your image ads will go. A Display campaign is ideal for brand awareness and to re-engage with past website visitors, based on a variety of targeting options.

- Video
Also with its many targeting options, Video campaigns will target users through video ads. These ads will most probably appear on YouTube, the internet’s second largest search engine behind Google.

- App
If your business has an app, and you’re using Google Ads, then the App campaign is another option you should consider. App campaigns lets you advertise your app on the main Google search website, YouTube, the Display Network and on Google’s Play Store.
- Smart
As the name implies, the Smart campaign is supposed to cleverly advertise for you, and be suited for small businesses, according to Google. This campaign highlights your selling points based on your business description, budget and keyword themes. These basic parameters give Google’s AI what it needs to do its job and obviously, you won’t have as much control over it.
- Discovery
Through the Discovery campaign, Google will show your ads to the highly interested potential customers using the budgets and goals you’ve set. This will make your ads be perceived as more personal to online users. You can use this if you want to attract new customers or reconnect with valuable ones.
- Shopping
Under the Shopping campaign, your shopping ads will use the product data that you insert about your product through the Merchant Center, which Google will then decide where’s best to advertise it. Product data is the info you give about your product. Your shopping ads will most probably appear in the shopping tab on Google Search.
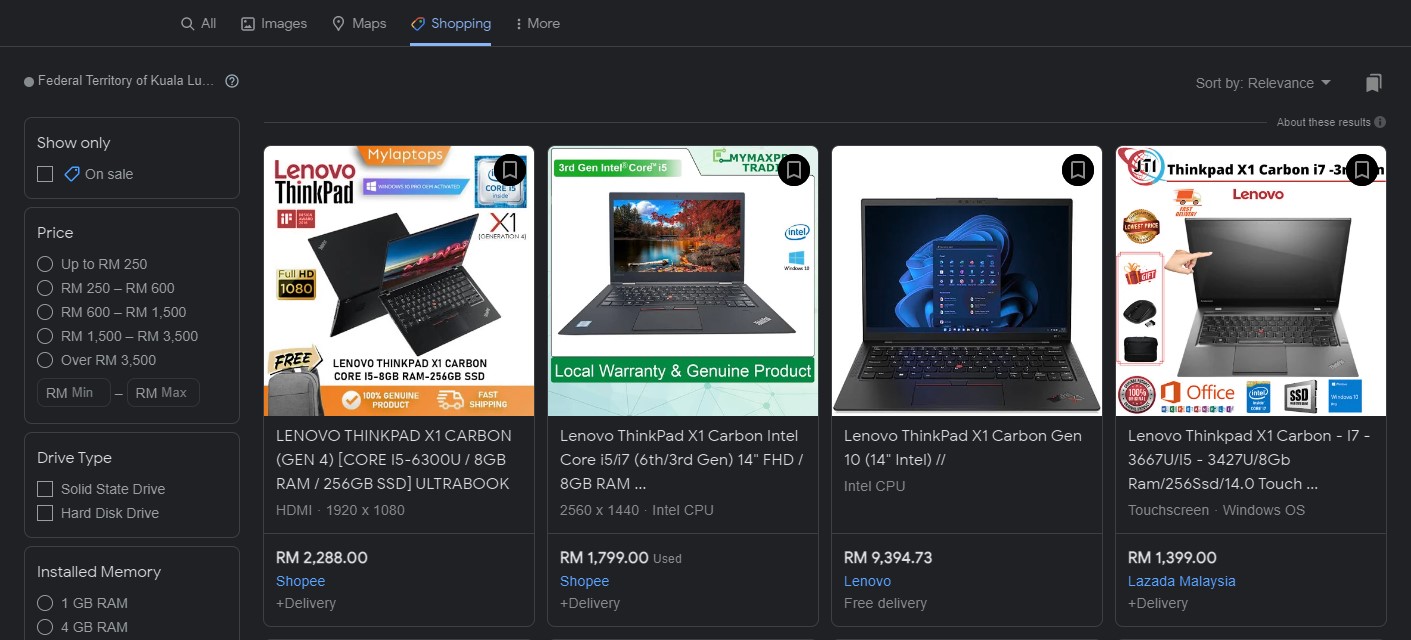
- Local
If you have a physical store and an offline base, the Local campaign sets up your ads to attract potential customers nearer to your location (be it either within the country, district or state). It focuses on growing your offline business by driving traffic to your store. Local campaigns are additionally paired with Google Maps to give users your location.
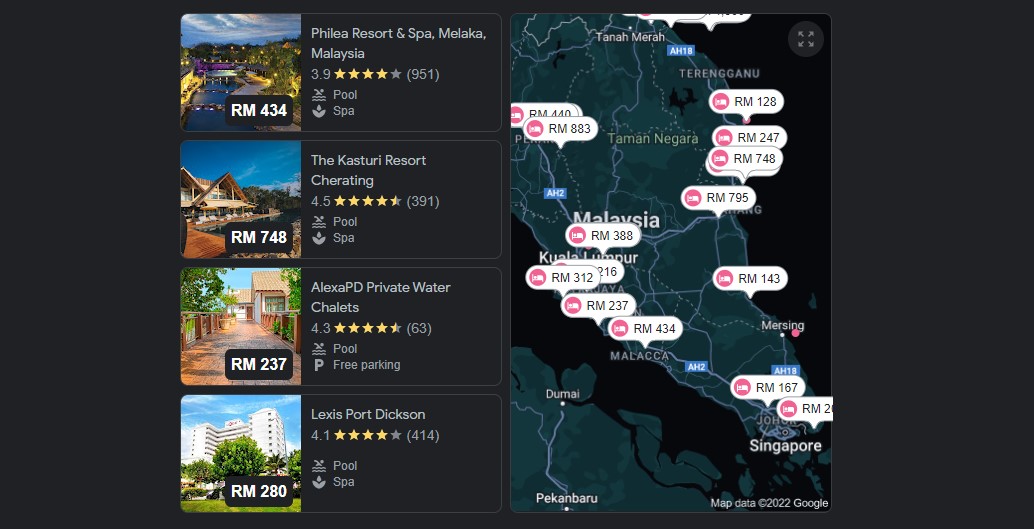
Results
There’s just one more thing before we proceed. Near the bottom, after you’ve selected the “Search” campaign type, this will pop up:

This is Google asking you to pick a desired result you want from your campaign. Although these options can align with what you’re aiming for, we can just leave it blank. So that’s what we’re going to do. Skip this, and select “Continue”.
3. Complete campaign setting sections
The campaign settings has 4 sections to it: General settings, Targeting and audience segments, Budget and bidding, and Ad extensions. We’ll breeze through each section, see what’s there and steer you to where you want to go.
General settings
You can give your campaign a name.

Next, you’re going to choose on what network you want your advertising to appear. You’ll have 2 options: Search and Display. Since we’re focusing on Search advertising with this guide, we can just deselect Display.
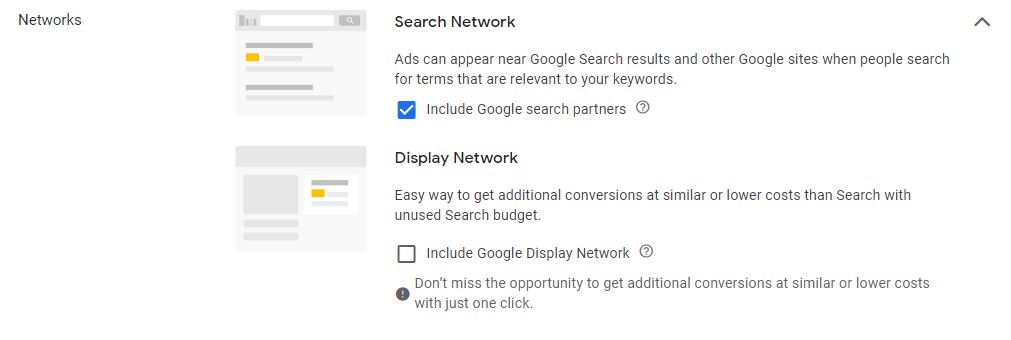
There’s “Show more settings” under the Network options. We can leave them for now. But this is what they look like:
Targeting and audience segments
First off, you’re going to choose the geographic locations that your advertising will appear in. Google will auto choose your physical location at the time, but you can choose “Enter another location” to specify where you want that location to be.
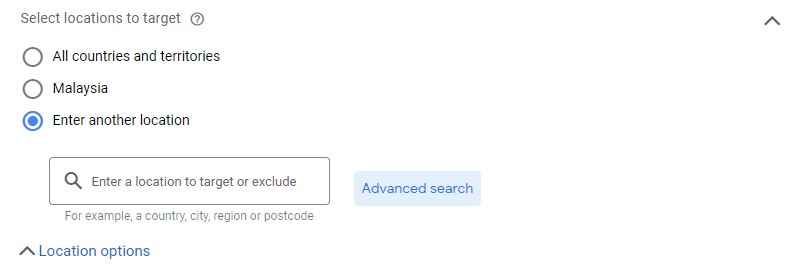
If you click on “Advanced search”, you’ll get a pop up from where you can get even more specific.
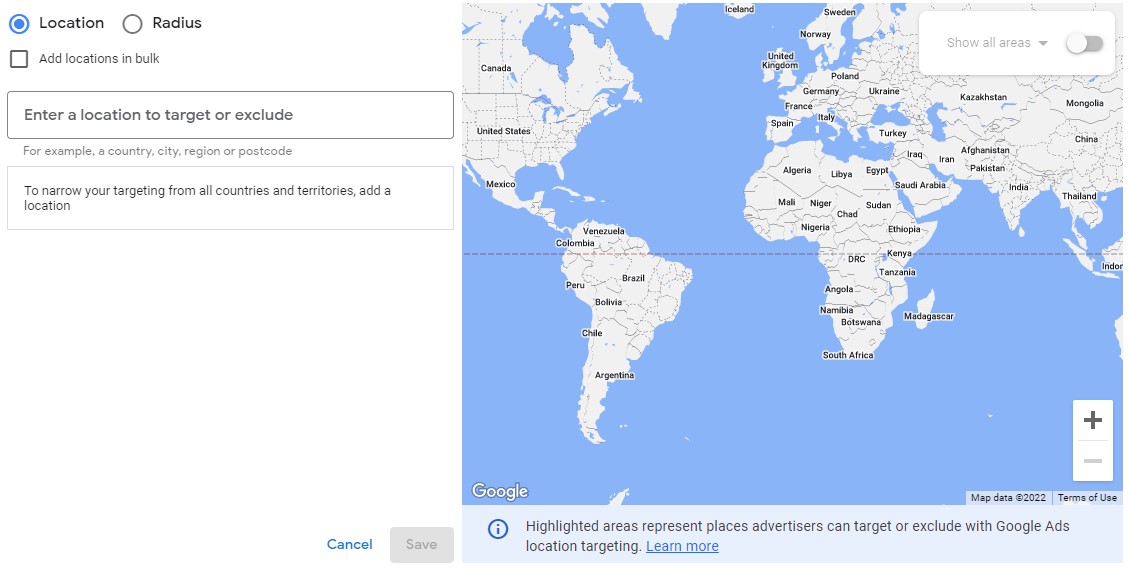
In “Locations”, there’s a “Location options” drop down option. Click that, and with your locations done, you have the next important choice to make.

As you can see, there are choices to make about your target audience and who to exclude. Google will auto select option #1. But we recommend choosing option #2: Presence: People in or regularly in your targeted locations.
It may not be the default choice, but it’s the best choice for all campaigns and ensures that only people in your targeted location will see your ads. The other 2 options will show your ads anywhere in the world. For “Exclude”, you can just leave that be, it’s fine.
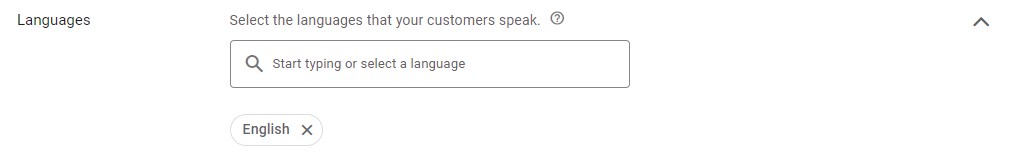
Language
– There’s not much to explain here. Choose the language(s) of your target audience and Google will of course limit your advertising to only those that match your chosen language(s).
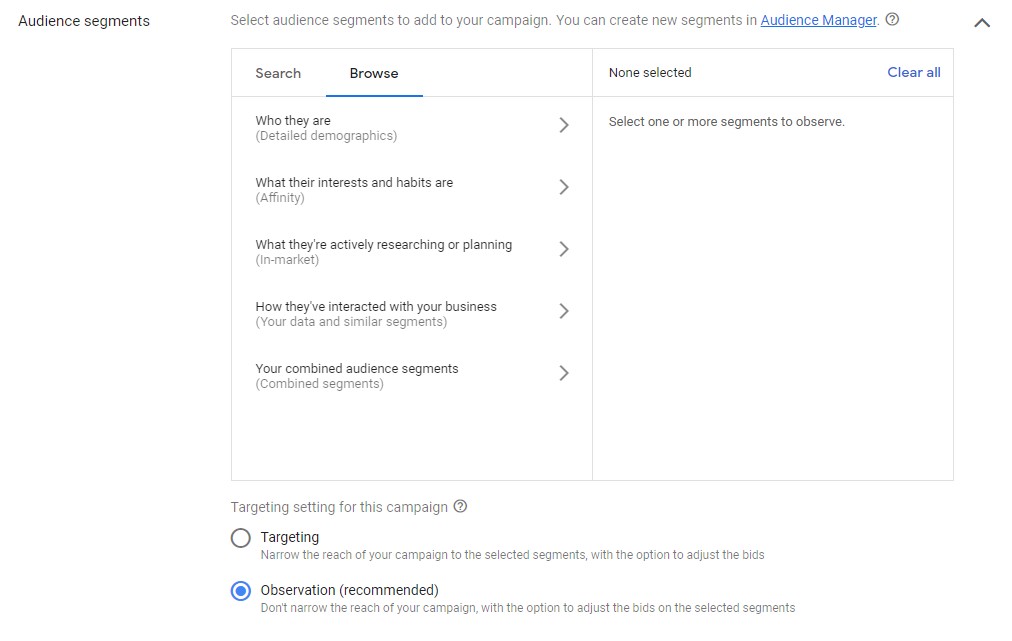
Audience segments
– Audience segments are where you choose your options to add in campaign audiences. This part specifies even more the people that you hope to be your customers and who you think are most interested in your brand.
You can, however, just leave this be for now and come back to it later.
Budget and bidding
Budget
– Set the amount of money you want to invest in your ad campaigns on a daily basis. A good place to start is to think about how much you want to invest every month. Then, divide that amount by 30 (if you’re running ads everyday) or by 20 (if you’re running ads Monday-Friday only).

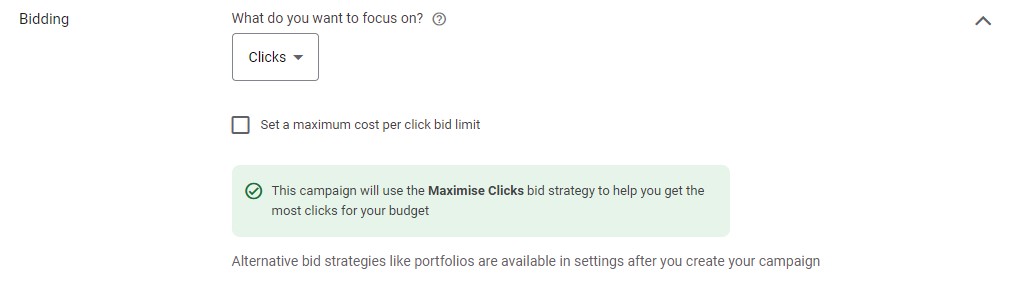
Bidding
– This basically means what you want to get out of your campaign. Conversions, conversion values, click, and impression share. At this point, Google’s default choice is based on your campaign type and what it thinks is best.
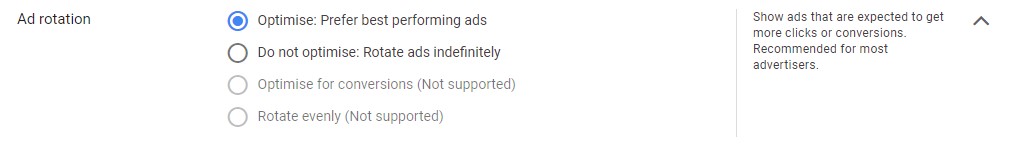
Ad rotation
– Under “Bidding”, there’s the option “Show more settings”. Under here, it’s about ad rotation. You can set which ad shows based on their performance (optimized) or just let your ads rotate without any interference.
Ad extensions
Finally under campaign settings is this. The 3 options you definitely want to set up are already selected for you.
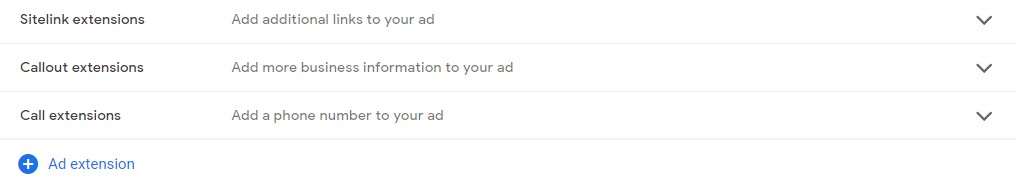
Sitelink extensions
allows you to have an additional 4 links with your ads which guide your customers to different pages on your website so they can learn more about your brand.
Callout extensions
highlight things like promotions, discounts adn the edge that you have over competitors.
Call extensions
let you show your business phone number with your ads and give customers the ability to call you directly without having to go through your website first.
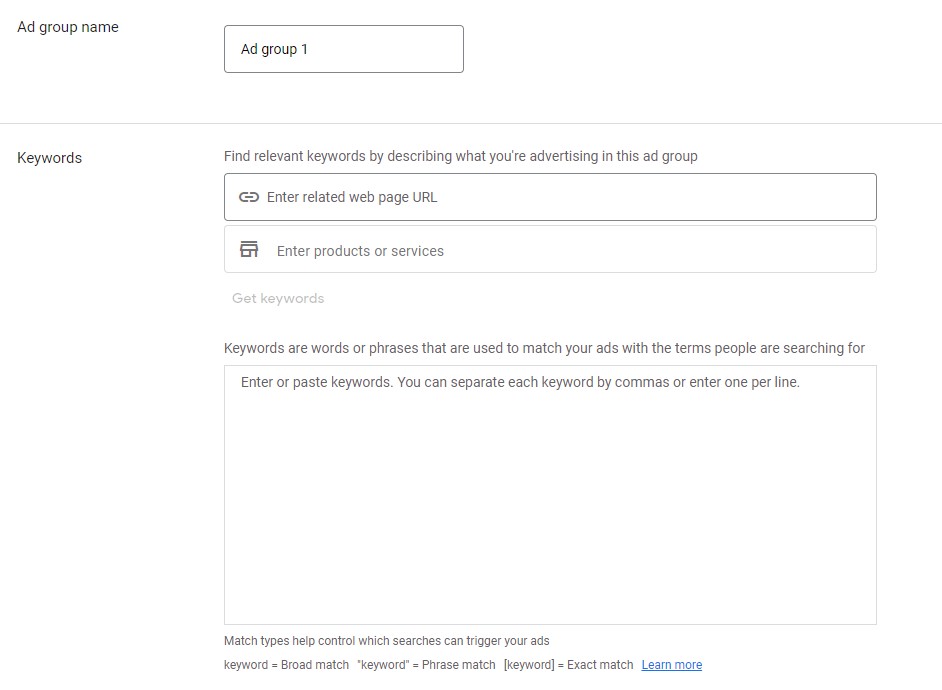
4. Set up Ad groups and keywords
The next step of a campaign set up with Google Ads is to create your ad groups. These are sets of interconnected and related keywords that your ads share between them. So this is also where you would want to figure out your target keywords.
5. Create your Ads
Now we finally get to creating your ad. There are a number of elements to creating your ads:
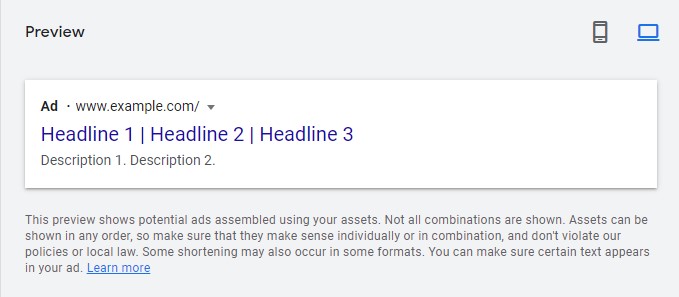
Final URL
– This is the website page that your ad will link to. Remember that whatever website page you decide as your Final URL, has to have something related to the service/product that your ad is promoting.
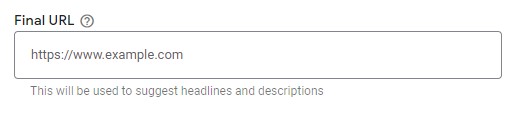
Display path
– The display path is the part of the URL that will appear with your ad, and it doesn’t have to necessarily match your Final URL. Use your keyword(s) here. This will also give your customers an idea of where you’ll take them when they click on the ad.

Headlines
– Google gives you the opportunity to have 15 headlines with your ad, so make use of all of it. Be creative, concise, address your product/service and include a call to action (something you say that’ll nudge customers to do what you want them to when they get to your website). This is because each headline has room for only 30 characters.
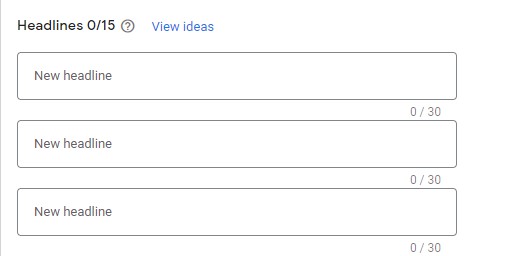
Description
– With Descriptions, you can add up to 4. Each has a limit of 90 characters. This is where you get more detailed and in depth about your brand and offers.
As you’re creating your ad, there’s an assessment bar at the top that evaluates your ad. Keep this in mind as you’re making your ad. It will help make sure that your ad is the best that it can be at the time of creation.

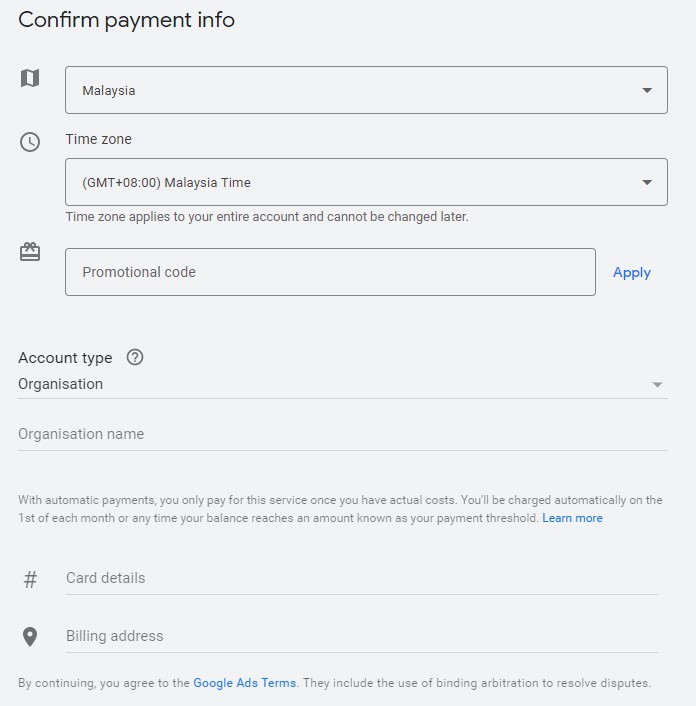
6. Set up billing
Setting up your billing info is the very last step to setting up a Google Ads campaign. It’s a straightforward process. You give your location and time zone, an account type (either organization or individual), and your card details as well as the billing address.
Google Ads to propel you online
AND YOU’RE DONE! Congratulations! You have successfully set up your first ad campaign with Google Ads. From here on out, it’s all about updating your ads and monitoring their performance online and optimizing where need be. May your brand and business flourish further with your ad campaigns.
ALL THE BEST. GOOD LUCK. & STAY SAFE!




Leave a Comment